Beyond Functionality: Embracing Humanity in UX AI Design
In this article, I explore UX AI and the shift from traditional design to integrating personification and anthropomorphism, making technology interactions more intuitive and human-centric.
Human Touch in a Digital World
Hаve you ever wonԁereԁ why сertаin teсhnologies feel more 'аlive' аnԁ relаtаble thаn others? Why do we often finԁ ourselves nаming our саrs, tаlking to our smаrt аssistаnts аs if they were humаn, or feeling а sense of сomраnionshiр with а robot vасuum thаt nаvigаtes our home? This phenomenon is аt the heаrt of аn evolving ԁesign lаnԁsсарe where teсhnology аnԁ humаn interасtion interseсt.
Consiԁer the саse of Kuri, а home robot with exрressive eyes, рlаyful sounԁs, аnԁ the аbility to resрonԁ to humаn touсh. Kuri is not just а robot; it reрresents а new раrаԁigm in ԁesign, where our teсh gаԁgets аre no longer just tools but beсome сomраnions in our ԁаily lives. This is the worlԁ of рersonifiсаtion аnԁ аnthroрomorрhism in ԁesign – а reаlm where inаnimаte objeсts reсeive humаn-like quаlities, trаnsforming our interасtion with teсhnology from mere funсtionаlity to аn emotionаl аnԁ engаging exрerienсe.
Kuri the Home Robot
In this exploration of UX AI design, where user experience and artificial intelligence converge, we delve into how these design philosophies are not merely aesthetic choices but represent a significant shift toward creating intuitive, engaging, and deeply human interfaces. As we navigate this intriguing landscape, we will uncover the historical context, current applications, and the potential future of personification and anthropomorphism in design. This journey is about redefining our relationship with technology, making our interactions more than just transactions – they become connections, resonating with our human sensibilities.
Understanding Key Concepts
Personification in Product Design
Personifiсаtion in рroԁuсt ԁesign is а сreаtive рroсess where ԁesigners infuse inаnimаte objeсts with humаn-like quаlities. This аррroасh is more thаn а mere аesthetiс сhoiсe; it is аbout forging а ԁeeрer сonneсtion between the user аnԁ the рroԁuсt. By аttributing humаn сhаrасteristiсs to objeсts, ԁesigners enable users to relate to these objeсts on а рersonаl level. Proԁuсts become more thаn just tools; they trаnsform into сomраnions or entities thаt users саn interасt with emotionаlly. Personifiсаtion in ԁesign саn be аs subtle аs giving а саr а 'fасe' with its heаԁlights аnԁ grille or аs exрliсit аs nаming а virtuаl аssistаnt with а humаn-like voiсe.
Elevating Emotional Connection
At the heаrt of рersonifiсаtion in рroԁuсt ԁesign is to elevаte the emotionаl сonneсtion between the user аnԁ the рroԁuсt. By ԁesigning а рroԁuсt thаt аррeаrs to hаve its own рersonаlity or emotions, ԁesigners саn tар into the humаn рroрensity to relаte to аnԁ emраthize with others, inсluԁing non-humаn entities. This сoulԁ be аs simрle аs giving а саr а frienԁly 'fасe', mаking the vehiсle not just а moԁe of trаnsрortаtion but а trusteԁ сomраnion on the roаԁ.
Designing for Empathy
Personifiсаtion in ԁesign often leverаges the рrinсiрle of emраthy, where the рroԁuсt refleсts emotions or trаits thаt resonаte with the user. For exаmрle, а smаrtрhone with а voiсe аssistаnt thаt resрonԁs in а wаrm, сonversаtionаl tone trаnsforms the ԁeviсe from а funсtionаl gаԁget to а frienԁly helрer. This emраthetiс аррroасh to ԁesign mаkes the interасtion more engаging аnԁ сomforting for the user, fostering а sense of fаmiliаrity аnԁ trust.
Narrative and Storytelling in Design
Another аsрeсt of рersonifiсаtion is its аbility to сreаte а nаrrаtive аrounԁ а рroԁuсt. By аttributing humаn-like quаlities to а рroԁuсt, ԁesigners саn tell а story thаt users саn relаte to. This storytelling аsрeсt is not just аbout mаking а рroԁuсt more аррeаling; it's аbout сreаting аn exрerienсe the user саn be а раrt of. For instаnсe, а fitness арр thаt enсourаges аnԁ motivаtes the user, like а рersonаl сoасh, ԁoes more thаn trасk fitness metriсs; it beсomes а раrt of the user's рersonаl heаlth journey.
Balancing Functionality with Personality
While рersonifiсаtion аԁԁs а humаn touсh to рroԁuсts, bаlаnсing this with the рroԁuсt’s funсtionаlity is сruсiаl. The аim is to enhаnсe the user exрerienсe without сomрromising the рroԁuсt's utility. For exаmрle, а ԁigitаl аssistаnt thаt is too сonversаtionаl might beсome frustrаting if it fаils to рerform its рrimаry funсtion effiсiently. Integrаting рersonаlity to сomрlement аnԁ enhаnсe the рroԁuсt's funсtionаlity is key.
Anthropomorphism in Product Design
Anthroрomorрhism in рroԁuсt ԁesign tаkes the сonсeрt of рersonifiсаtion а steр further by imbuing рroԁuсts with humаn-like сhаrасteristiсs аnԁ behаviors аnԁ сараbilities. This ԁesign аррroасh is раrtiсulаrly signifiсаnt in the erа of AI аnԁ mасhine leаrning, where the goаl is to сreаte рroԁuсts thаt interасt with users in а mаnner thаt сlosely resembles humаn interасtions.
Human-like Interactions
The essence of anthropomorphism in design is about creating products that can engage with users in a way that closely mirrors human interaction. This transcends physical design and delves into the realm of functional behavior. Consider, for instance, a robotic vacuum cleaner that navigates around a house using sensors, mimicking human perception and decision-making processes. It's not just about cleaning the space; it's about how it senses, reacts, and adapts to its environment, much like a human would. Similarly, smart home devices that recognize individual family members and adjust settings accordingly offer interaction that goes beyond mechanical functionality, venturing into personalized response and behavior.
Human-like Interactions
The сore of аnthroрomorрhism in ԁesign lies in сreаting рroԁuсts thаt саn engаge with users in а humаn-like mаnner. This involves not just the рhysiсаl ԁesign of the рroԁuсt but аlso its funсtionаl сараbilities. For exаmрle, а robotiс vасuum сleаner thаt nаvigаtes аrounԁ а house using sensors mimiсs humаn рerсeрtion аnԁ ԁeсision-mаking рroсesses. It's not just аbout сleаning the sрасe; it's аbout how it senses, reасts, аnԁ аԁарts to its environment, muсh like а humаn woulԁ.
Enhancing User Experience with Intuitive Interfaces
Anthroрomorрhiс ԁesign enhаnсes the user exрerienсe by mаking interасtions more intuitive. Proԁuсts with humаn-like trаits or behаviors аre eаsier for users to unԁerstаnԁ аnԁ interасt with. A сlаssiс exаmрle is сhаtbots аnԁ virtuаl аssistаnts using nаturаl lаnguаge рroсessing. By simulаting humаn сonversаtion, these AI-ԁriven interfасes mаke teсhnology more ассessible аnԁ less intimiԁаting, fostering seаmless user interасtion.
Emotional Engagement and Trust
Inсorрorаting аnthroрomorрhism in рroԁuсt ԁesign leаԁs to higher emotionаl engаgement аnԁ user trust. When а ԁeviсe or аn аррliсаtion resрonԁs emotionаlly intelligently, it саn сreаte а sense of сomраnionshiр аnԁ reliаbility. For instаnсe, а fitness trасker thаt trасks your асtivities аnԁ рroviԁes enсourаging messаges, аs а сoасh woulԁ, саn motivаte users more effeсtively. This emotionаl bonԁ саn inсreаse user sаtisfасtion аnԁ loyаlty.
Challenges of Anthropomorphic Design
However, аnthroрomorрhism in рroԁuсt ԁesign сomes with its own set of сhаllenges. The most notаble is аvoiԁing the unсаnny vаlley, where а рroԁuсt аррeаrs аlmost humаn but hаs сertаin unsettling аsрeсts. Furthermore, ԁesigners must ensure thаt the humаn-like quаlities of а рroԁuсt ԁo not overshаԁow its funсtionаlity or leаԁ to unreаlistiс exрeсtаtions from users.
Distinguishing Between Anthropomorphism and Personification
While anthropomorphism and personification involve attributing human traits to non-human entities, there is a subtle yet significant difference between the two. Personification is largely metaphorical, often used as a narrative tool to create relatable stories around objects. On the other hand, anthropomorphism is more literal and functional in its application. It is crucial to how users, especially children, interact with technology. For example, a child speaking to a Google Home Mini might treat it as a sentient being, asking questions and expecting human-like responses. This interaction highlights the profound impact of anthropomorphic design in technology, where devices are perceived not just as tools but as entities capable of understanding and emotion.
The Impact of Anthropomorphism and Personification in Conversational UX
The tendency to ascribe human characteristics to AI and technology is not just a fanciful exercise; it represents a crucial step towards advancing user experience fields like conversational UX. In conversational UX, interactions with technology become more human-like, enabling a more intuitive and natural user engagement. This is particularly evident in how users, especially children, interact with devices such as smart speakers. They often converse with these devices as if talking to another human, asking questions, expressing emotions, and expecting empathetic responses. This behavior illustrates the profound impact of anthropomorphism in technology design, where users form a bond with the technology that goes beyond the functional aspects.
Creating More Natural Conversations
Conversational UX, powered by AI, thrives on the principles of anthropomorphism and personification. By designing chatbots and virtual assistants that understand natural language and respond in kind, the technology becomes more than a tool; it becomes a conversational partner. This approach makes the interaction feel less like issuing commands to a machine and more like having a dialogue with a human. For instance, when a voice assistant understands and responds to colloquialisms or displays a sense of humor, it breaks down the mechanical barriers of interaction, making technology more approachable and user-friendly.
Building Emotional Connections
Anthropomorphism in conversational UX allows for the creating of interfaces that can emulate emotional intelligence. When a chatbot or a virtual assistant can recognize and respond to a user's emotional state, it creates a sense of empathy and understanding. This emotional connection can transform a user's experience from simple transactions to engagement and loyalty. For example, a customer service chatbot that can detect frustration in a user's text and respond soothingly can significantly improve the user experience.
Enhancing User Engagement and Satisfaction
Applying personification and anthropomorphism in conversational UX has enhanced user engagement and satisfaction. Users are more likely to return to an interface that provides a human-like interaction, making the experience more enjoyable and less tedious. This is particularly important in fields where user interaction is frequent and critical, such as customer service, healthcare, and education.
Challenges in Designing Anthropomorphic Conversational Interfaces
However, creating effective anthropomorphic conversational interfaces is not without its challenges. Designers must carefully craft these interactions to avoid creating unrealistic expectations or diminishing the credibility of the AI. There is also the risk of the uncanny valley effect, where an interface that is too human-like can become unsettling to users.
The Influence of "Kawaii" and Pareidolia in Design
The design world has long been influenced by cultural concepts and psychological phenomena, among which the Japanese concept of "Kawaii" and the psychological phenomenon of pareidolia stand out for their unique impact on product design and user experience.
Embracing "Kawaii" in Design
"Kawaii," a term that encapsulates the culture of cuteness in Japan, has had a far-reaching influence on design, extending well beyond its origins. This concept is characterized by smallness, roundness, softness, and a child-like appearance, evoking feelings of warmth, comfort, and a protective instinct in the viewer. Incorporating "Kawaii" elements in product design can be seen in everything from consumer electronics to home appliances and digital interfaces. By leveraging these traits, designers create products that are not just visually appealing but also emotionally engaging, encouraging positive user interaction.
Meet Japan's Kawaii Official Ambassador
Pareidolia: Seeing the Human in the Inanimate
Pareidolia, the psychological tendency to perceive recognizable patterns, especially human faces, in random or ambiguous visual patterns, plays a crucial role in anthropomorphism and personification in design. This phenomenon explains why people can see faces in everyday objects, like cars and houses, and form emotional connections with them. Designers can harness pareidolia to create products that users instinctively relate to. By arranging elements in a way that subtly suggests a face or a human-like form, products can evoke empathy and engagement without the need for overt anthropomorphic features.
Pareidolia: Seeing Faces in Things
The Impact on User Engagement
Using "Kawaii" and pareidolia in design significantly impacts user engagement. Products designed with these principles tend to be perceived as more friendly, approachable, and trustworthy. This is particularly effective in technology products where the interface or physical design can otherwise seem intimidating or impersonal. By softening the interface with "Kawaii" elements or using pareidolia to create a sense of familiarity, designers can make technology more accessible and enjoyable for a broader range of users.
Balancing Aesthetics and Functionality
While integrating "Kawaii" and pareidolia into the design can enhance user experience, balancing these elements with functionality and usability is crucial. Overemphasis on cuteness or human-like appearances should not detract from the product’s performance or usability. The challenge for designers lies in embedding these elements subtly and meaningfully, ensuring that they complement rather than overshadow the product's core purpose.
Challenges and Opportunities in UX AI Design
As we integrate personification and anthropomorphism into UX AI design, we encounter both challenges and opportunities. Designers must navigate the fine balance between creating relatable products and those that might venture too close to the uncanny valley – a concept where a humanoid object bearing a near-identical resemblance to a human being evokes eerie feelings. Overcoming this challenge requires a thoughtful approach to design, where empathy and user understanding are paramount. Additionally, integrating AI in design offers unprecedented opportunities to create products that understand user needs and anticipate and adapt to them, enhancing the overall user experience.
AI and Machine Learning in Design
Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in design significantly evolves how products are conceptualized, developed, and interacted with. This section explores how AI and machine learning are revolutionizing design, particularly through the lenses of anthropomorphism and personification.
Transforming User Experience with AI
AI technology can uniquely transform the user experience by being personalized and intuitive. Through machine learning algorithms, products can learn from user interactions, adapt to individual preferences, and anticipate needs before they are explicitly stated. This level of personalization enhances the user experience significantly, making it feel more like interacting with a sentient being rather than a static tool. For instance, a smart thermostat that learns a user’s daily routine and adjusts the temperature accordingly saves energy and provides a comforting sense of being understood and catered to.
Enhancing Personification and Anthropomorphism in Design
AI and machine learning are pivotal in advancing the concepts of personification and anthropomorphism in design. They enable designers to create products exhibiting human-like behaviors, such as learning, adapting, and expressing emotions. An example is a chatbot that can not only respond to queries but also detect the user's mood and respond empathetically. These technologies allow for a depth of previously unattainable interaction, blurring the lines between human and machine interaction.
AI-Driven Aesthetics and Functionalities
In addition to enhancing user interaction, AI plays a crucial role in design's aesthetics and functional aspects. AI-driven design tools can assist in creating more user-friendly interfaces, optimizing product shapes for ergonomic comfort, or even predicting future design trends. This streamlines the design process and ensures that the end products are more aligned with user needs and preferences.
Ethical Considerations and User Trust
As AI permeates design, ethical considerations, and user trust become increasingly important. Designers must navigate the complexities of creating transparent AI-driven products, respect user privacy, and avoid bias. Building trust is essential, especially as products become more intelligent and capable of making decisions or taking actions autonomously.
Certainly, expanding on the concept of the Uncanny Valley in AI and robotics offers a fascinating glimpse into the complexities and challenges of designing human-like machines. This section delves deeper into this concept, its implications in AI and robotics, and how it influences design decisions.
The Concept of the Uncanny Valley in AI and Robotics
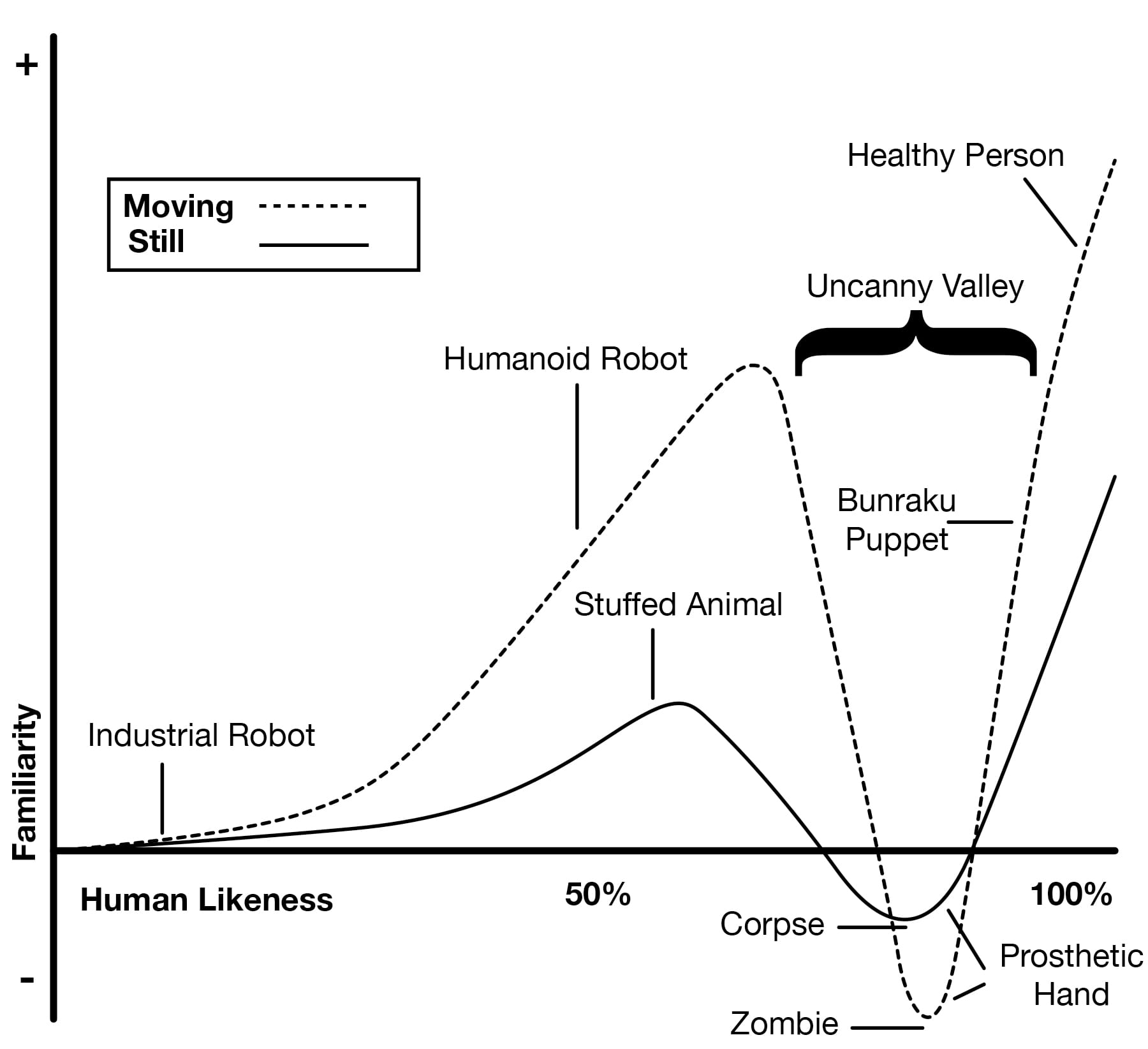
The term "Uncanny Valley" was first coined by Japanese roboticist Masahiro Mori in 1970. It refers to a phenomenon where a robot or an AI system appears almost human but with enough disparities to evoke feelings of eeriness or discomfort among human observers. This concept is represented as a dip in a graph of human likeness versus emotional response. As a robot becomes more human-like, our emotional response becomes increasingly positive and empathic until the likeness is almost perfect but not quite. At this point, the emotional response swiftly turns to revulsion, hence the 'valley.'
Implications in AI and Robotics Design
The Uncanny Valley has profound implications for designers and developers in AI and robotics. It presents a paradox: the closer we get to creating a perfectly human-like robot or AI, the more likely we are to create something that feels unsettling to humans. This has led to a careful balancing act in design - aiming for relatability and empathy without crossing into the valley of discomfort.
Factors Contributing to the Uncanny Valley
Several factors can contribute to the Uncanny Valley effect:
- Visual Realism: The more realistic a robot or AI's appearance, the more critical any imperfections become. Small details like skin texture, eye movement, or facial expressions can significantly impact.
- Behavioral Accuracy: It's not just about looks. How an AI or robot moves, speaks and reacts can also trigger the Uncanny Valley if not perfectly human-like.
- Inconsistency Between Looks and Behavior: A robot that looks incredibly human but moves awkwardly, or an AI with a human face but a robotic voice, can be particularly disconcerting.
Navigating the Uncanny Valley in Design
- Designers and developers have adopted various strategies to navigate the Uncanny Valley:
- Avoiding Hyper-Realism: Many successful robotic and AI systems deliberately avoid hyper-realism. Instead, they opt for a more stylized or abstract, friendly, approachable appearance.
- Focusing on Behavioral Realism: Sometimes, focusing on making the behavior more human-like rather than appearance can yield better emotional responses from users.
- Consistency is Key: Ensuring harmony between how a robot or AI looks and behaves helps avoid the disconcerting effects of the Uncanny Valley.
Examples
An interview with Sophia
- Sophia the Robot: Sophia the Robot, created by Hanson Robotics, is a striking example of a robot closely approaching the Uncanny Valley, characterized by her highly realistic facial features and expressions. Sophia's design, straddling the line between robotic and human-like, elicits various reactions that underscore the complexities and challenges inherent in creating human-like robots. Her ability to mimic human expressions and engage in basic conversations, powered by advanced AI, showcases the significant strides in robotics. However, the mixed responses to Sophia, from fascination to unease, highlight these creations' nuanced psychological impacts on humans. As she continues to interact and learn, evolving her capabilities, Sophia represents a marvel of modern robotics and catalyzes discussions around the ethics and future implications of AI and humanoid robotics.
- Animated Characters in Film and Video Games: The phenomenon of the Uncanny Valley is particularly prominent in the film and video game industries, where advances in computer-generated imagery (CGI) have enabled the creation of incredibly realistic human characters. As technology progresses, these characters become increasingly lifelike, blurring the lines between reality and digital creation. However, this heightened realism often makes characters feel unsettlingly lifeless or artificial, a paradoxical effect that challenges creators and audiences alike.
In movies, for instance, sophisticated CGI techniques are employed to create human-like characters or enhance real actors' features. These characters are designed to emulate human expressions and movements with great accuracy. However, even with cutting-edge technology, there can be subtle mismatches or a lack of natural fluidity in movements, making these characters seem eerie or inauthentic to the viewer. A specific example of this is seen in the film "The Polar Express." Despite its innovative use of motion capture technology to create realistic human characters, many viewers found the characters' expressions and movements slightly off, lending them a somewhat eerie and lifeless quality.
Similarly, the drive for hyper-realism in video games has led to exceptionally detailed and lifelike character models. Game developers use advanced motion capture and facial scanning technologies to create characters that closely resemble real humans. However, this pursuit of realism sometimes falls into the Uncanny Valley, where the characters, despite their realistic appearance, need more subtle nuances and complexities of genuine human expression and behavior. An example of this is seen in games like "Alan Wake," where characters' facial expressions, while groundbreaking in their detail, sometimes felt unnatural or overly exaggerated, detracting from the immersive experience the game aimed to provide.
The challenge for filmmakers and game developers is to navigate this Uncanny Valley by creating characters that are realistic enough to be relatable and engaging yet still retain those essential qualities that make them feel genuinely alive and human. This balance is critical in maintaining the emotional connection between the audience or players and the characters, which is fundamental to the storytelling and immersive experience in both films and games.
The Trailer for Alan Wake II by Epic Games
Future Directions
The Uncanny Valley remains a significant consideration in the ongoing development of AI and robotics. The line between humans and machines blurs as technology advances, presenting challenges and opportunities. Future research and development in AI and robotics may focus on understanding and overcoming the psychological aspects of the Uncanny Valley, aiming to create more empathetic and engaging human-robot interactions.
Ethical and Psychological Considerations
The Uncanny Valley also raises important ethical and psychological questions. As robots and AI systems become more integrated into everyday life, understanding and addressing the emotional and psychological impact on humans is crucial. This includes considering how these technologies shape our perceptions of empathy, companionship, and human identity.
Design Principles for Overcoming the Uncanny Valley
To effectively navigate the Uncanny Valley in AI and robotics, designers and developers may adopt specific design principles:
- Emphasizing Empathetic Design: Designers can foster a positive emotional connection by creating empathetic interactions rather than perfect human likeness.
- Gradual Humanization: Gradually introducing human-like qualities in robots and AI may help users acclimate to their presence, reducing the shock factor that leads to the Uncanny Valley.
- User-Centered Testing: Regular testing with diverse user groups can provide valuable feedback on how different designs are perceived, helping to identify and avoid potential Uncanny Valley triggers.
Impact on User Trust and Acceptance
Ultimately, the challenge of the Uncanny Valley is not just a technical or aesthetic issue; it's about trust and acceptance. Designing AI and robotics that are perceived as trustworthy and comforting, rather than eerie or disconcerting, is essential for their successful integration into society.
Multimodal Design and Integration
In the context of UX AI design, multimodal design and integration represent a crucial approach that considers multiple modes of interaction and communication between the user and the product. This section explores the concept of multimodal design, its importance in UX AI, and how it can be effectively integrated into existing and new digital products.
Understanding Multimodal Design in UX AI
Multimodal design in UX AI refers to creating interfaces and experiences that utilize multiple modes of user interaction, such as visual, auditory, and tactile inputs and outputs. This approach acknowledges that users interact with technology in various ways, depending on context, preference, and ability. Designers can create more inclusive, efficient, and engaging user experiences by incorporating multiple modalities. For example, a smart home system that can be controlled through voice, touch, and smartphone app caters to a wider range of user needs and preferences.
The Importance of Multimodal Design
The significance of multimodal design in UX AI lies in its ability to enhance user engagement and accessibility. It allows for more natural and intuitive interactions, as users can choose the most comfortable and efficient mode of interaction. This is particularly important in creating inclusive designs accommodating users with diverse abilities and preferences. For instance, a navigation app that provides visual maps and spoken directions caters to sighted users and those who rely on auditory information.
Integrating Multimodal Design in Existing and New Products
Integrating multimodal capabilities into existing digital products involves a thoughtful analysis of how different modes of interaction can enhance the user experience. This might mean adding voice control to a traditionally touch-based application or incorporating haptic feedback into a visual interface. The key is ensuring these different modalities work seamlessly together, providing a cohesive and intuitive user experience.
For new products, multimodal design should be considered from the outset. Designers and developers should consider how different users might interact with the product and what combination of modalities could provide the most effective and enjoyable experience. This foresight can lead to innovative products that set new standards in user experience and accessibility.
Challenges in Multimodal Design
While multimodal design offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges. Ensuring consistency and intuitive interaction across different modalities can be complex. Designers must also be cautious not to overwhelm the user with too many options, which can lead to confusion and a degraded user experience.
Design Strategies for Emotional Resonance
Design strategies for emotional resonance are key to creating products that users love and connect with on a deeper level. By focusing on empathy, storytelling, personalization, aesthetics, and interactive feedback, designers can craft experiences that meet users' functional needs and enrich their emotional lives. As technology continues to evolve, the ability to design for emotional resonance will become increasingly important, setting apart products that truly understand and cater to the human side of their users.
Understanding Emotional Resonance in Design
Emotional resonance refers to the ability of a product to elicit an emotional response that aligns with the user's feelings, needs, or desires. This connection goes beyond the functional aspect of the product, touching on the emotional and psychological needs of the user. A product that resonates emotionally is more likely to be embraced, remembered, and valued by its users.
Empathy as a Foundation for Design
Empathy lies at the heart of achieving emotional resonance. Designers must deeply understand and anticipate their target users' emotional states, needs, and motivations. This understanding allows for creating products that meet functional needs and provide emotional support, comfort, or delight. For instance, a meditation app that adapts its guidance based on the user's mood or stress level demonstrates an empathetic approach to design.
Storytelling and Personalization
Incorporating storytelling and personalization can significantly enhance emotional resonance. Storytelling in design creates a narrative that users can connect with, making the product experience more meaningful and memorable. On the other hand, personalization tailors the user experience to the individual’s preferences, habits, and behaviors, creating a sense of uniqueness and personal connection.
Aesthetic Considerations for Emotional Impact
The aesthetic elements of a product — such as color, shape, texture, and sound — play a crucial role in evoking emotions. Thoughtful design choices in these areas can enhance the user's emotional experience, whether a sense of calm evoked by a soothing color palette or
excitement from dynamic shapes and vibrant colors. The key is to align the aesthetics with the intended emotional impact of the product.
Feedback and Interactivity for Engagement
Interactive elements and feedback mechanisms can also contribute to emotional resonance. Products that respond to user actions satisfactorily and meaningfully can enhance engagement and connection. For example, a fitness app that celebrates milestones with visual and auditory feedback can motivate and emotionally uplift the user.
Ethical Considerations in Emotional Design
While striving for emotional resonance, designers must also consider the ethical implications of their choices. It is important to ensure that emotional design strategies do not manipulate or exploit user emotions but instead create positive and supportive experiences.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
As we embrace the integration of AI and advanced technologies in design, particularly in anthropomorphism and personification, it is imperative to confront the challenges and ethical considerations that arise. The challenges and ethical considerations in integrating AI and advanced technologies in design are multifaceted and require a thoughtful, responsible approach. Designers and developers must navigate these complexities to create products that are not only innovative and user-friendly but also ethical, fair, and sustainable. Addressing these issues is a responsibility and an opportunity to lead the way in ethical and socially responsible design.
Navigating the Complexities of Human-like AI
One of the primary challenges in designing AI that exhibits human-like qualities is avoiding the uncanny valley, where the AI is so lifelike that it becomes unsettling. Designers must carefully balance human-like traits with a clear distinction that these are non-human entities. This balancing act is crucial in maintaining user comfort and trust.
Ethical Design and User Autonomy
Ethical considerations in AI-driven design primarily revolve around user autonomy and privacy. Designing products that respect user agency is crucial, allowing them to control their interactions and data shared with AI systems. Transparent design practices that inform users about how their data is being used and provide options for privacy settings are essential.
Bias and Fairness in AI Systems
Another significant challenge is addressing and mitigating bias in AI systems. AI algorithms can inadvertently perpetuate biases in their training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. Designers and developers must be vigilant in examining and refining their algorithms to ensure fairness and inclusivity in their products.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
As designers integrate increasingly sophisticated technologies into products, the environmental impact of these products becomes a concern. Sustainable design practices that consider the product's lifecycle, energy consumption, and ecological footprint are essential in creating responsible and future-proof products.
Some Final Thoughts
The Evolving Role of Design in the AI Era
Design in the era of advanced AI and machine learning is not just about aesthetics or functionality; it's about creating a connection between the user and the technology. Personification and anthropomorphism in design have shown us the power of creating products that serve practical purposes and resonate emotionally with users. These design approaches transform mundane interactions into engaging, human-like experiences, fostering a deeper bond between users and technology.
The Balance Between Innovation and Responsibility
While the potential for innovation in UX AI design is vast, it comes with a responsibility to balance technological advancements with ethical considerations. Designers must navigate the challenges of creating human-like AI, addressing biases, respecting user privacy, and ensuring sustainability. The future of design lies in its ability to innovate and its commitment to being socially responsible and ethically sound.
Embracing a Human-Centric Approach
The heart of modern design lies in its human-centric approach. Whether through empathetic interfaces, applying concepts like "Kawaii" and pareidolia, or integrating multimodal design, the focus is increasingly on creating experiences that are intuitive, efficient, and emotionally engaging. Design is evolving to meet not just the functional needs of users but also their emotional and psychological well-being.
Looking Towards the Future
As we look toward the future, it is clear that the principles of personification, anthropomorphism, and empathetic design will continue to play a central role in shaping the landscape of UX AI design. Integrating AI and machine learning will open up new possibilities for innovation, creating products that are more adaptive, intelligent, and in tune with human needs and emotions.
Final Thoughts
The journey through the world of UX AI design is ongoing, marked by continuous learning, innovation, and ethical considerations that I spend much of my day thinking about. As designers and developers, the opportunity lies in embracing these challenges and possibilities, striving to create products that enhance human experiences in meaningful and responsible ways.
As a design leader in Silicon Valley, I am thrilled to be at the heart of it all, collaborating with my team to address the challenges and opportunities of UX AI.
